
Bicycle lights explained: the light beam
12 February 2025
In this blog, we explain all the ins and outs of our lights. All their unique features, and we explain how lights work. We created three different blogs, all about a specific feature of bicycle lights. This blog tells you everything about the light beam. The others explain more about a bicycle light's batteries and the Lumen, candela, and Lux.
How a light is emitted into the world can be done in several ways. Our designers have made specific choices for each light to create the optimal experience for you. But they also keep an eye on how the light influences other traffic on the street. Different situations ask for different designs. A light beam can be spread out in a wide beam to cover a big area, or it can be compressed into a very narrow, bright beam.
From the source into the darkness
Let's start at the beginning! Light is created by the LEDs inside the lamp. There are multiple ways to guide the light outside. For example by using lenses and/or reflectors. Here, the real high-end designing, experience, and research & development come in.
It is relatively easy to create a powerful light, but the real issue is what is done with all that power afterwards. A very powerful light is often also a very heavy and unpractical light. It is therefore important that all that power is used as efficiently as possible. This way we can design lights that give you the best coverage of light without being too heavy or unpractical. You will get the most useful light out of the Lumen that is emitted from the light source.

The goal of a light beam
As you have read above, creating a very strong and powerful light is one thing, but using all that power in your favor may be just as important. A light beam supports you on your ride. The light beam should cover the important spots ahead of you so that you can create an overview of the world around you in the dark. Different situations ask for different light coverage. Below we will give you a few examples to get an idea of how light might work for you:
A dark MTB-track
When riding your bike on a dark MTB track, it is obviously important to have good vision straight in front of you. You want to make sure you won't hit any obstacles like trees, fences etc. Another thing to keep in mind though, think about the fact that MTB tracks are often very twisty with a lot of sharp corners and difficult passages. A good overview of the world around you is therefore also very important. You need a light with a high amount of lumen, that is also spread out of a wide light beam. This way you will be able to safely ride your bike along with obstacles by seeing what is ahead of you, as well as knowing what is further to the side of you.
Dark roads
When riding your bike on dark roads. Side visibility is less important. You need good visibility straight ahead of you to make sure you don't miss any potholes, sticks, or other obstacles on the road. A narrower light beam will be suitable for you as you need light further ahead of you, but not as much to the sides.
Urban roads
When riding your bike through cities and on well-lit roads, you probably don't need a light to see for yourself. The world around you creates enough light for you to be able to safely ride your bike. You still need lights though, to make sure other traffic knows you are there. It is very important to be visible to other traffic from all angles. A good way to establish that is through the use of a light with a wider light beam so that you will be visible from a wider angle. Besides, you don't want to blind other traffic with your incredibly bright light. A headlight with an oval light beam spreads out the light a bit wider and avoids shining into other people's eyes.
The reflector
Now that you understand the importance of the efficiency of your light beam we can dive a bit deeper into how this efficiency is created. One part of the puzzle is the type of reflector that is used to guide the light into the darkness.
The light that is emitted from an LED shines in all directions. It is up to the housing of the light to make sure the light is guided in the right direction without losing too much of it. This guiding can be done by three different reflectors, all with their pros and cons. Below, we will explain a bit more about these reflectors.
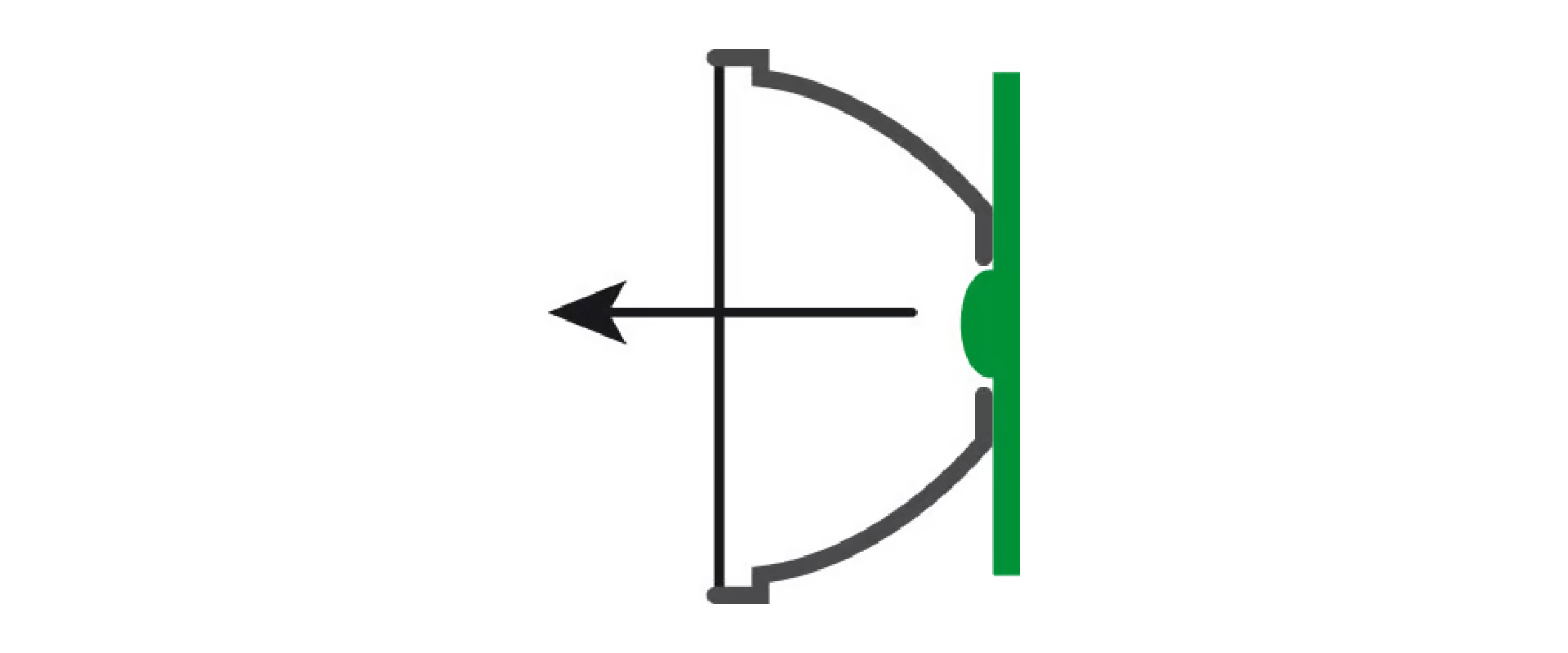
The classic reflector
A classic reflector is quite simple. Light that does not shine into the outside world will be caught by the reflective inside walls of the light to be reflected until it also ends up in the outside darkness and thus shines out of the lamp. This way, all light that is emitted by the light source makes it to the outside world. This solution is relatively cheap, but there is not much control over the way that light is emitted. It can shine in any direction. So even though all the light makes it to the outside world, there is often no symmetrical and well-designed light beam pattern.
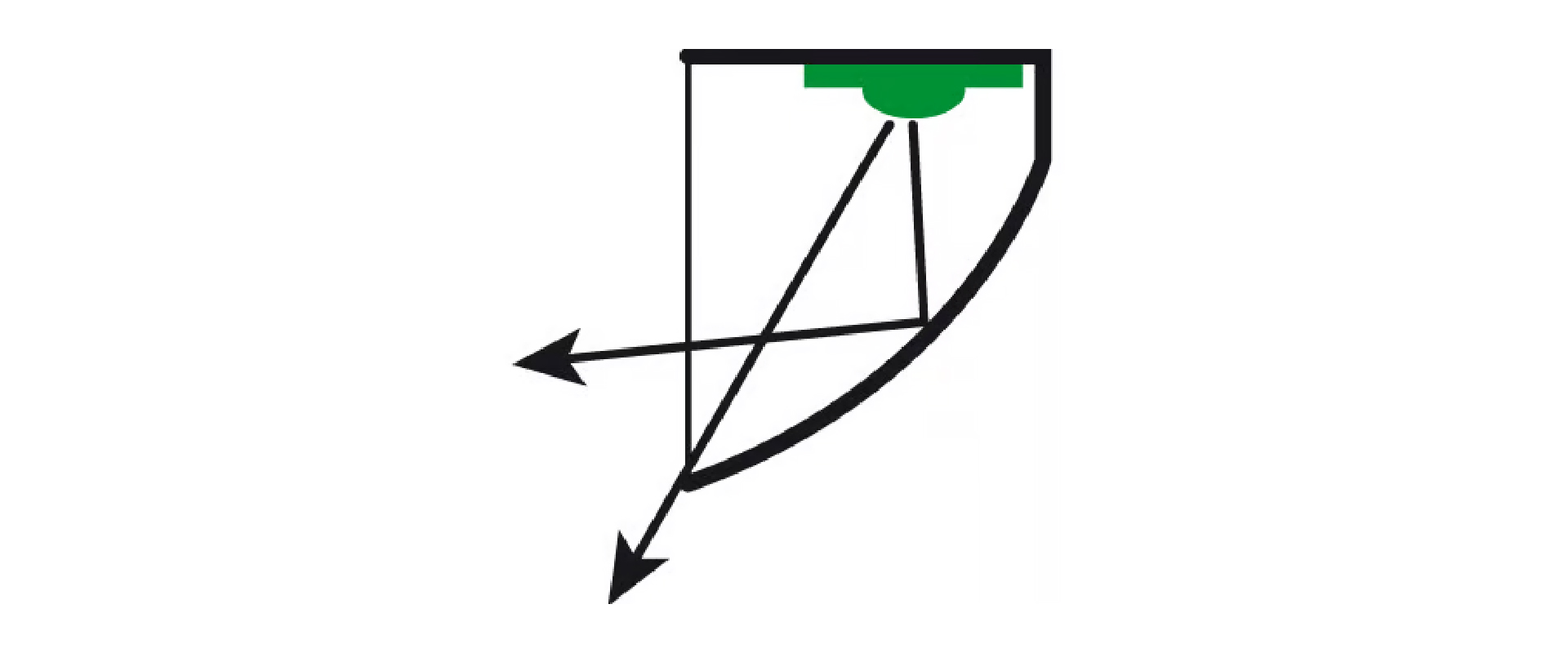
The modern reflector
A modern reflector is a very clever way to guide the light beam. With this type of reflector, the LED is placed at an angle in the housing where it cannot shine a direct light beam out of the lamp. The light is first caught by a reflector that then reflects the light out of the lamp in a controlled manner. This way, all the light shines in a very controlled way in a light beam that is ingeniously designed.
A good example of the benefits of this is our own Stud headlight. Due to the indirect reflection of the light within the housing, the LED won't shine straight into other traffic, while still providing you with an abundance of light ahead of you. The Stud is specifically designed to not blind other traffic with the help of this clever reflector.
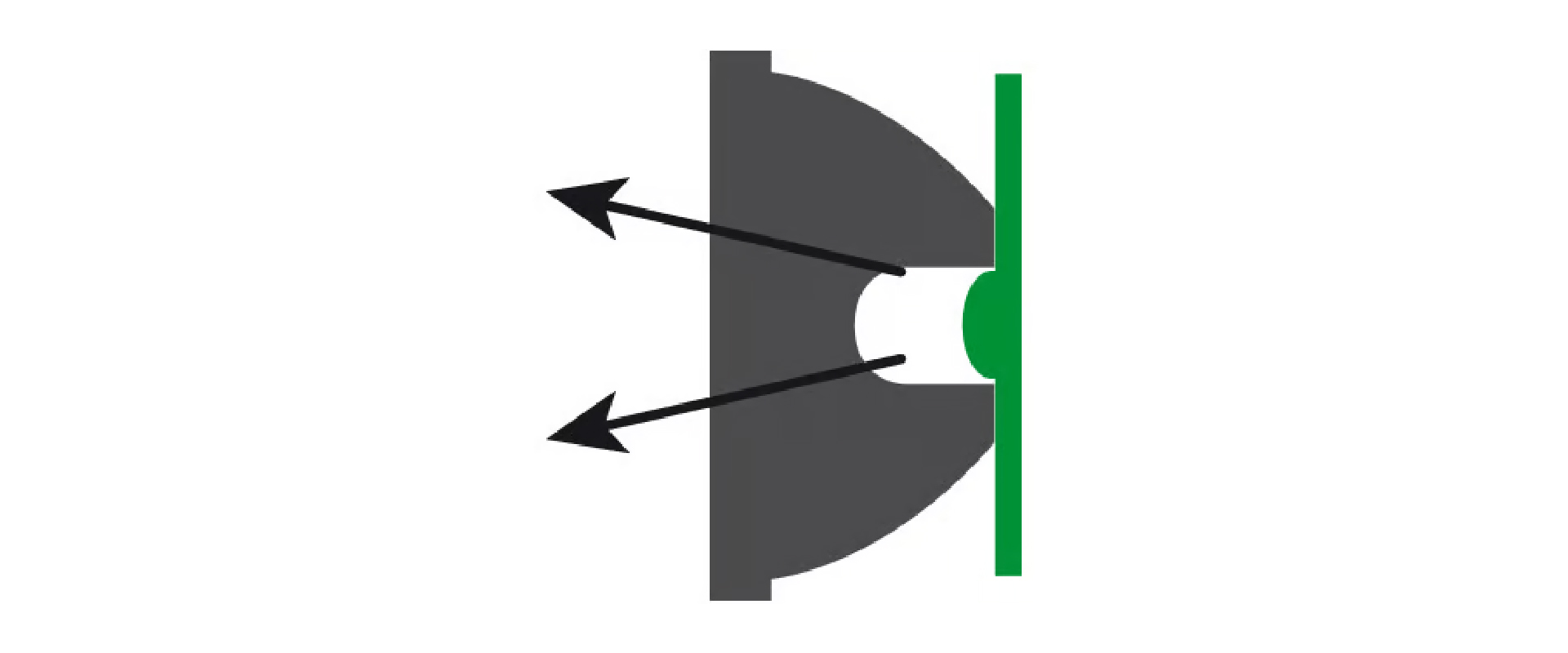
The optics
And then last but not least, the lens optics. Here, The LED's in the light will be completely surrounded by high-end optics that catch all the light that is emitted and spread this light into a nice and even light beam. The main benefit is that the light beam can be controlled very well and no light will be lost. This way, a nice light beam is created with an even grading towards the sides of the beam and a clear and bright hotspot.
Our NanoStrike and StrikeDuo series all contain these high-end optics. If you have read our other blog about Lumen, Lux and Candela, have seen that we aim for a specific amount of lux while the amount of lumen can vary to create the best user experience in different situations. Through the use of optics, this can be established.
Use the light beam in your favor
The optic lenses that we use really get our lights to a higher level. We can use the available lumen output completely in our favor. By placing vertical ridges on the optic lens of the StrikeDuo series, we are able to fully control the light and create a light beam in an oval beam pattern. This gives the rider a better light coverage ahead, while not affecting upcoming traffic.
Conclusion
And there you go! A bit more information about how a light beam can work in your favor and how we try to establish that. You have now a better understanding of how Lumen and an effective light beam are connected and hopefully, you understand that power is not everything. It is very important to know how all that power is bundled in an efficient light beam that supports you on your rides.
